
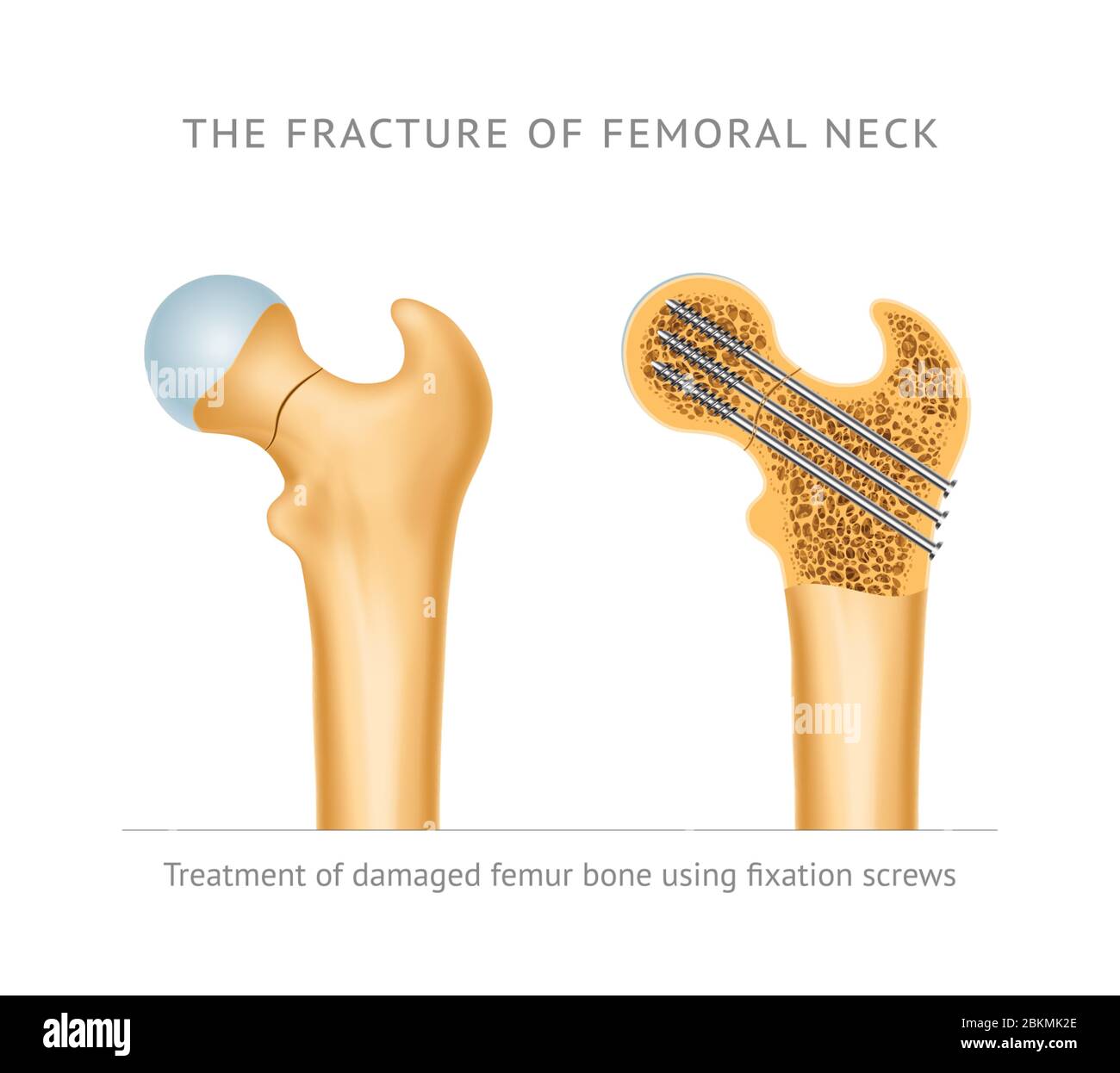
Cannulated screw fixation is appropriate for older children and adolescents.Smooth pin fixation may be acceptable for small, young children when supplemented with a spica cast.Closed reduction or open reduction is performed to achieve anatomic alignment.Appropriate for older children or with displaced fractures.

Considered for nondisplaced or minimally displaced fractures up to age 4 years.Closed reduction and spica cast immobilization.Treatment is determined by the Delbet classification, displacement, and the age and size of the patient. Capsulotomy has been recommended to evacuate the intracapsular hematoma and potentially decrease the risk of AVN. Treatment ranges from closed reduction and spica casting to open reduction and internal fixation. CT or MRI may play a role in concurrent femoral neck fracture-dislocations to better define the pattern of injury.(Lee 2010) When attempting a cross-table lateral radiograph, care should be taken to move the uninjured limb so as not to significantly displace the fracture on the injured side. Plain radiographs are the primary imaging modality to diagnose and classify a pediatric femoral neck fracture. They may have a shortened and externally rotated extremity, and the fracture may be associated with other polytrauma injuries (head injuries, abdominal injuries, etc).
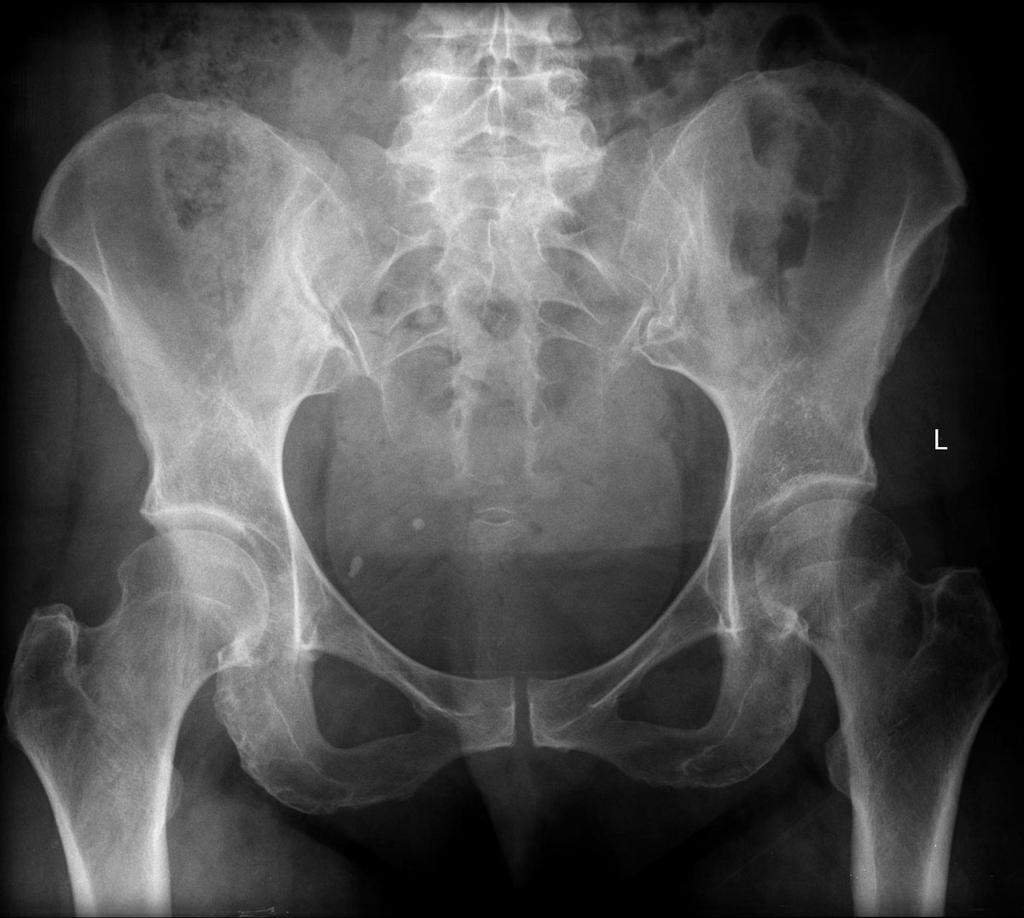
These patients are unable to bear weight on the injured extremity.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
